How to Use Parameters in autobotAI
What Are Parameters?
Parameters in autobotAI serve as dynamic data carriers that enable seamless communication between different actions within a workflow. By passing data from one node to another, parameters ensure flexibility, adaptability, and enhanced automation in workflows. They allow you to customize actions using real-time inputs or outputs from preceding steps, making your workflows more robust and efficient.
Why Use Parameters?
Incorporating parameters in your workflows provides the following benefits:
- Dynamic data handling: Enables the effortless transfer of data between nodes, ensuring workflows adapt to different scenarios.
- Customizability: Allows actions to be tailored based on the specific requirements or outputs of preceding nodes.
- Error minimization: Reduces the need for hardcoding, improving maintainability and minimizing errors.
- Scalability: Supports varied data inputs, making workflows suitable for large-scale operations without additional modifications.
- Enhanced debugging: Makes tracking and debugging easier by providing transparency in the data being passed.
How to Use Parameters in autobotAI?
Defining Parameters
Follow these steps to define and configure parameters in autobotAI:
- Select an Action: Choose the action where you want to add or modify parameters.
- Modify the Action: Click on the action and select the Modify option in the interface.
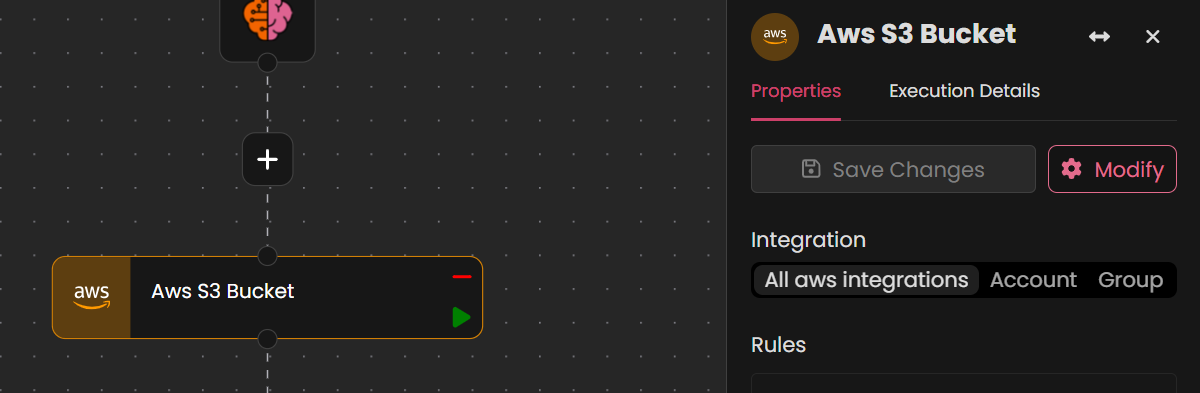
- Add Parameters: In the Parameters section, click the + Add button. A dropdown menu will appear, displaying all supported data types.
Parameter Types
autobotAI supports a variety of parameter types to enhance flexibility and customization in workflows. Below is a detailed explanation of each type:
Parameter Types
autobotAI supports a variety of parameter types to enhance flexibility and customization in workflows. Below is a detailed explanation of each type:
| Parameter Type | Description | Example/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Bool | Boolean value, representing true or false. | true, false |
| Date | A valid date, chosen through a date picker. | 2024-12-31 |
| JSON | Structured data in JSON format. Can represent objects or arrays. | { "key": "value" }, [1, 2, 3] |
| List | A list of values, each entered on a new line. | value1, value2, value3 |
| Number | A numeric value, either an integer or float. | 100, 5.5, -10 |
| String | A text string, which could also be a dynamic value pulled from a previous node. | hello world, {{node.output}} |
| Shell | Command-line scripts or shell commands. | echo "Hello World", ls -l |
| HCL | Configuration data in HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL). | resource "aws_instance" "example" {} |
| YAML | Data formatted in YAML syntax, typically used for configurations. | apiVersion: v1\nkind: ConfigMap\nmetadata:\n name: example-config |
| Handlebar JSON | Handlebars templating for generating JSON. | { "key": "{{value}}" } |
| Handlebar HTML | Handlebars templating for generating HTML content. | <html><body>{{content}}</body></html> |
| Handlebar Markdown | Handlebars templating for generating Markdown text. | # Title\nContent here {{value}} |
| Handlebar Text | Handlebars templating for plain text. | Item ID: {{id}} |
Configure Additional Details
-
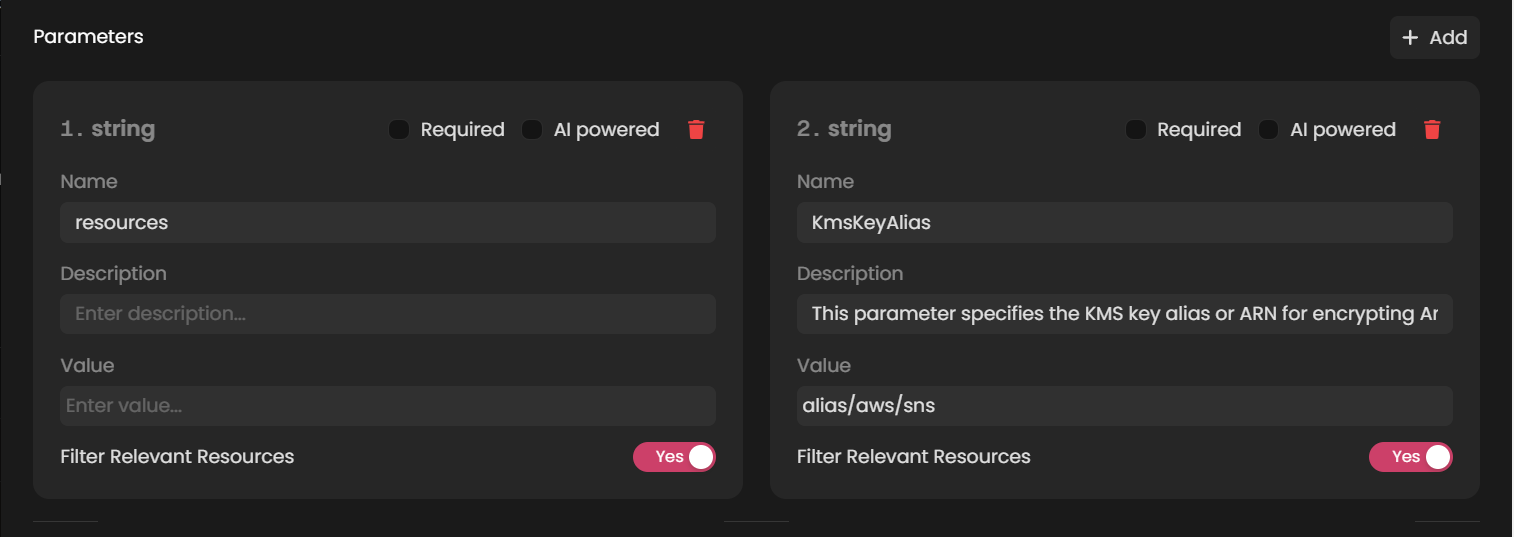
Provide Parameter Details: Enter the following details for each parameter:
- Name: A descriptive name for the parameter (e.g.,
resources). - Description: A brief explanation of what the parameter represents (e.g., "List of resources to process").
- Value: Specify how the parameter's value is passed, such as dynamic input from a previous node.
- Name: A descriptive name for the parameter (e.g.,
-
Required and AI-Powered Options:
- Required: Marks the parameter as mandatory. This is useful when the workflow cannot proceed without the value being provided.
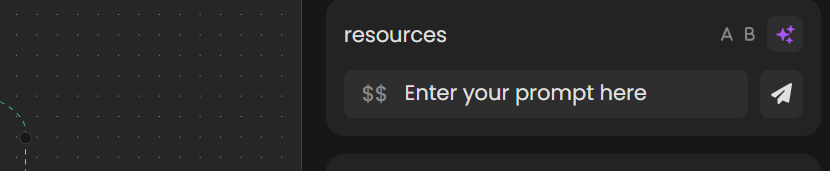
- AI Powered: Allows AI to dynamically generate parameter data based on a prompt.
Clicking the yellow sparkle button will prompt you to provide a custom prompt.
-
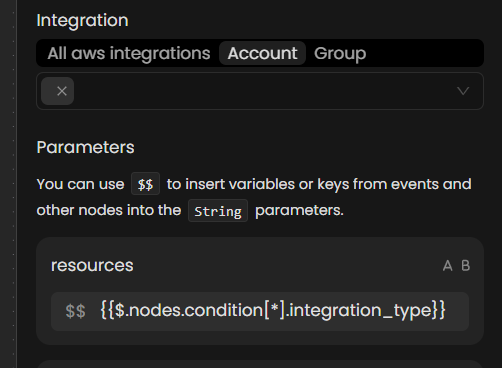
Filter Relevant Resources(Optional): Enable filtering of resources based on integration ID or region.
Example: Using JSON Path ($$) for Dynamic Node Referencing
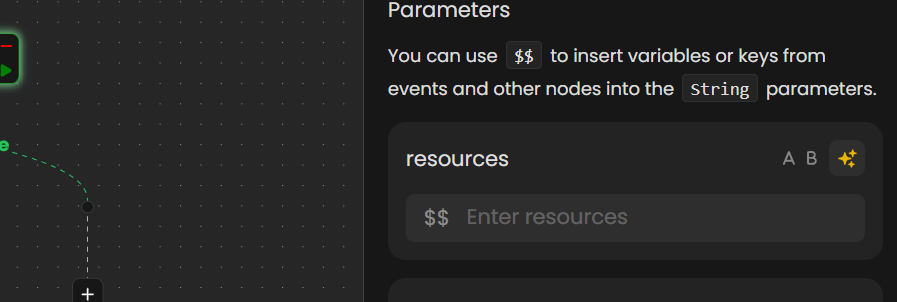
For the string data type, you can use the JSON Path selector to dynamically reference data from previous nodes. In the parameter interface, enter $$ in the parameter value field.
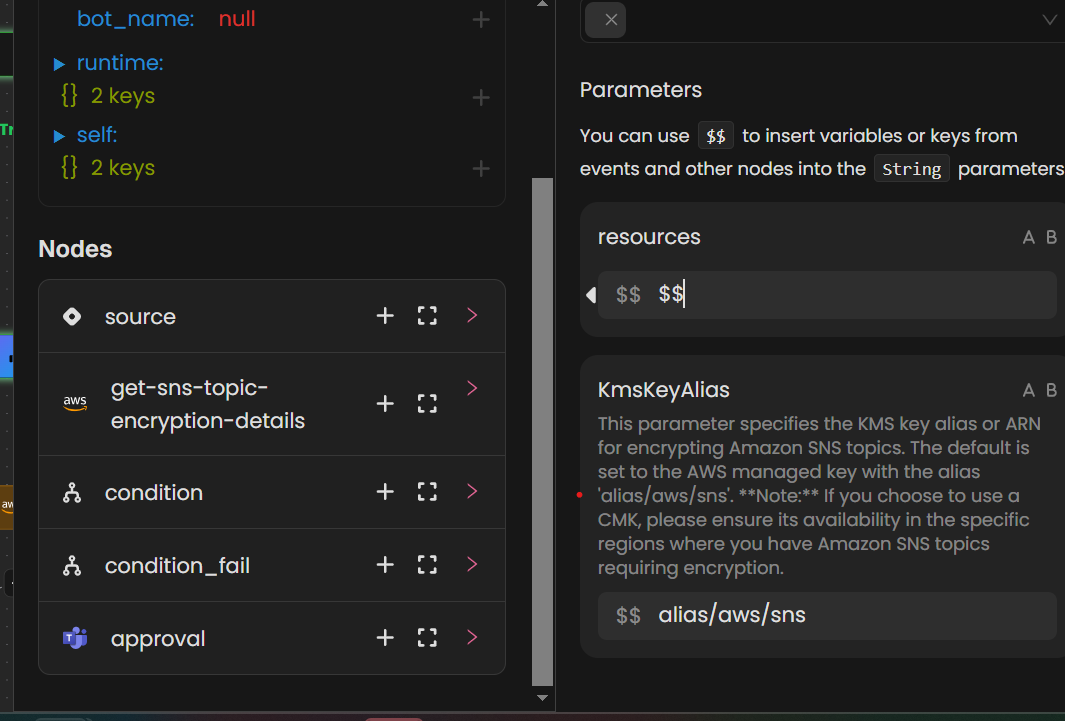
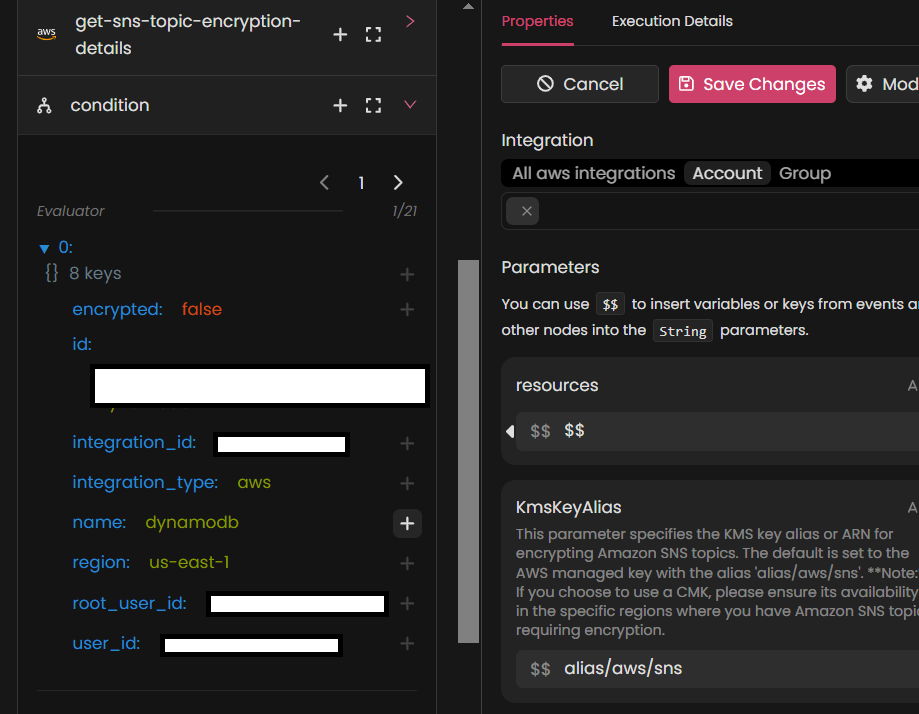
A pop-up will appear, displaying available nodes and their outputs. From the pop-up, you can select the desired node by clicking the + symbol next to the relevant field. This action allows you to pass the selected data as a parameter to the current action.
Best Practices for Using Parameters
- Use descriptive names: Clearly name parameters for easy understanding.
- Assign defaults: Provide sensible default values for optional parameters.
- Validate inputs: Ensure parameter values meet expected formats.
- Leverage types: Choose the right parameter type to simplify workflows.
