AI Agent Node
What is the AI Agent Node?
The AI Agent Node is your workflow's AI brain. It uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to think, reason, and make intelligent decisions within your automation workflows. Unlike standard nodes that follow fixed rules, the AI Agent can understand context, analyze data, and dynamically choose actions based on the situation.
Perfect for: Data validation, intelligent decision-making, content generation, alert analysis, and complex reasoning tasks.
Prerequisites
Before configuring AI Agent nodes in autobotAI:
- Have an AI provider account (e.g., OpenAI key). Set up in Integrations.
- Understand responsible AI. AI Guide.
- (Optional) For memory: Set embedding model in Settings > Preferences > AI Configuration.
Quick Start
Basic Setup in 3 Steps
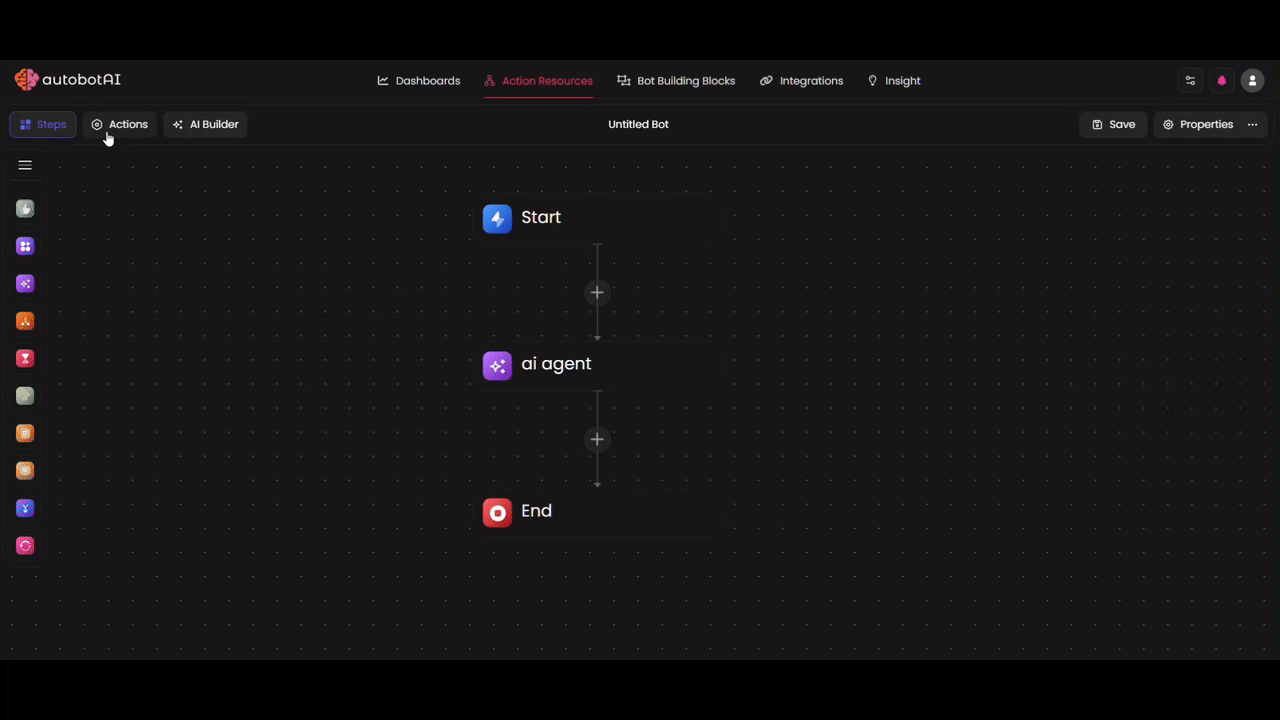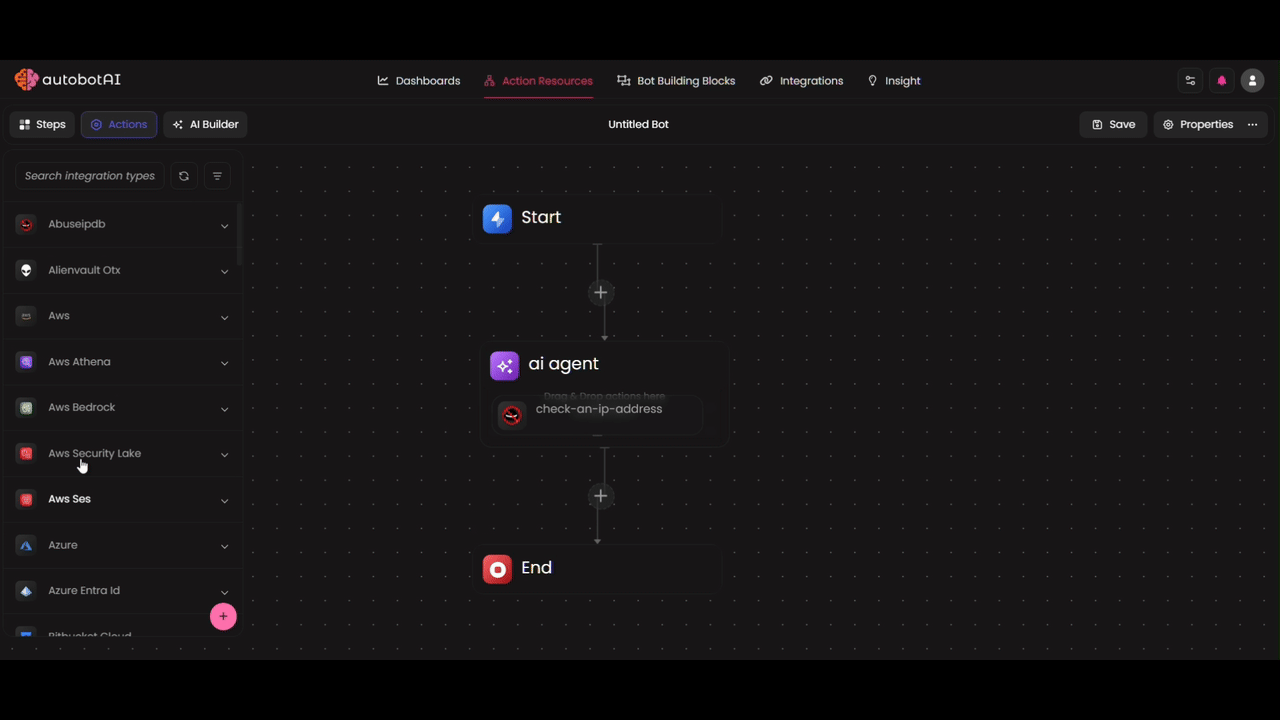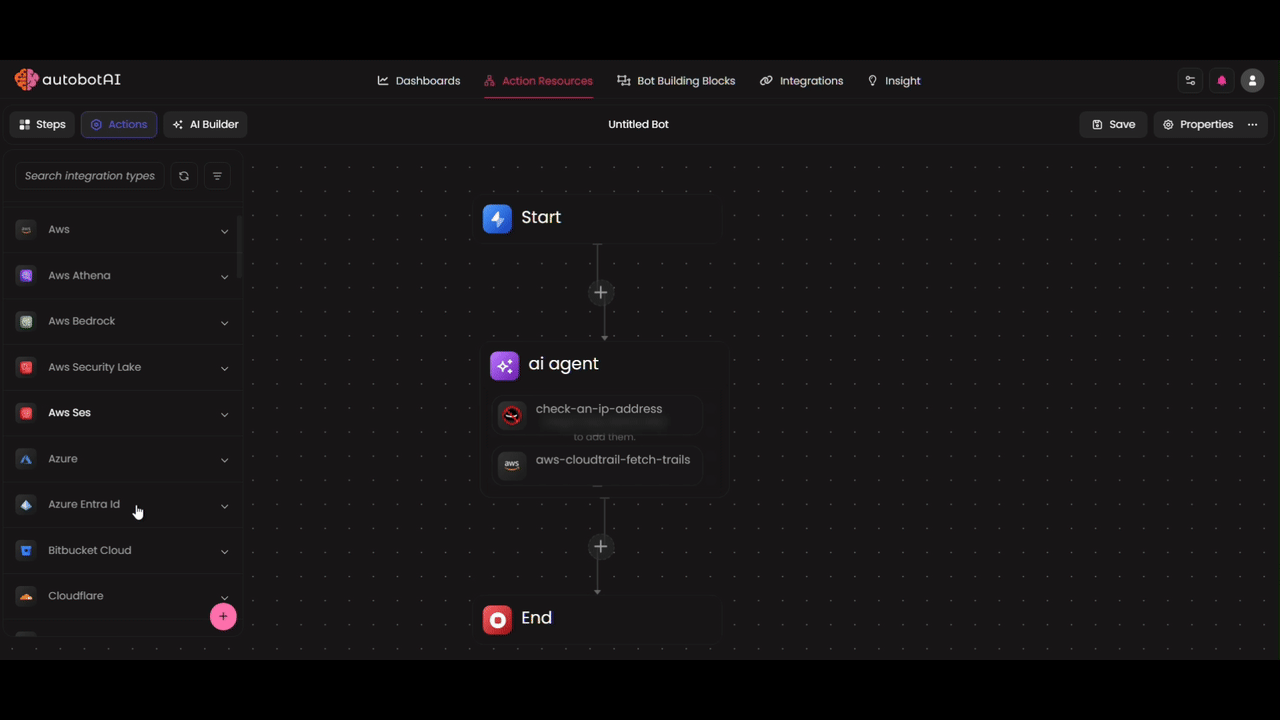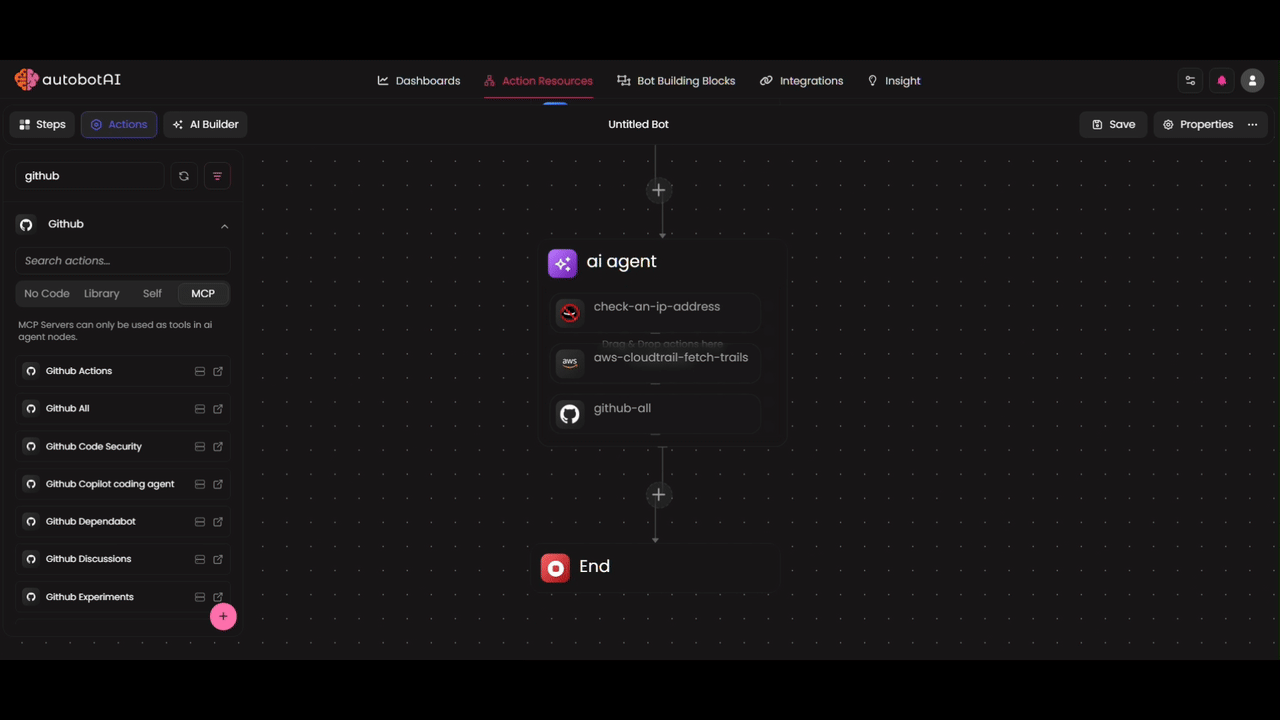
1. Add the Node
- Drag the AI Agent Node from your node library onto the canvas
- Connect it to your workflow
2. Configure AI Model
- Choose your LLM provider (OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, etc.)
- Select your model (GPT-4, Claude, etc.)
3. Write Your Prompts
- System prompt: Define the agent's role and behavior
- User prompt: Specify the task to perform
Configuration Guide
Essential Settings
Integration Type & ID
Choose which AI service to use:
- OpenAI (GPT-3.5, GPT-4)
- AWS Bedrock (Claude, Llama, Mistral)
- Custom integrations
LLM Model
Select the specific model based on your needs. The AI Agent Node supports any tool-calling enabled model from your configured integrations.
Supported Providers:
- ✅ OpenAI - All models (GPT-5, GPT-4o, GPT-4 Turbo, GPT-3.5, etc.)
- ✅ AWS Bedrock - All available models (Claude, Llama, Mistral, Titan, etc.)
- ✅ Custom Integrations - Request integration for your preferred AI provider
Model Selection Guide:
| Use Case | Recommended Models | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Complex reasoning & analysis | GPT-5, GPT-4o, Claude Opus, Claude Sonnet | Deep understanding, nuanced decisions |
| Fast, simple tasks | GPT-3.5, Claude Haiku, Llama 3 | Quick responses, cost-effective |
| Balanced performance | GPT-4 Turbo, Claude Sonnet, Mistral | Good speed-to-quality ratio |
| Privacy & compliance | AWS Bedrock models | Data stays in your environment |
💡 Tip: Any model that supports function/tool calling will work with the AI Agent Node. If your model can execute tools, it's compatible.
🔧 Custom Models:
- AWS Bedrock: Upload and use your own custom models directly through Bedrock
- Custom Integration: Request integration for your preferred AI provider or proprietary model by contacting support
Need a specific provider? Reach out to add custom AI integrations to your workspace.
System Prompt
The system prompt defines your agent's role, behavior, and guidelines. It's sent with every request to the LLM, so keep it concise to avoid context issues.
textYou are a security analyst assistant. Analyze alerts and determine if they are true positives or false positives. Be concise and provide clear reasoning.
What happens behind the scenes: Your system prompt is combined with internal instructions that enable tool usage, apply guardrails, and configure agent behavior. Your prompt takes precedence - it shapes how the agent interprets and executes tasks.
⚠️ Important: Keep system prompts focused and reasonably short. Very long system prompts (approaching context limits) can cause:
- Hallucinations or inaccurate responses
- Context rotting (losing track of important details)
- Slower processing times
💡 Best Practice: Aim for 100-500 words. Be specific about the role and key behaviors without unnecessary detail.
User Prompt
Tell the agent what specific task to perform with the input data:
textAnalyze this WAF alert: {{$trigger.alert}} Determine if it's a false positive and provide your confidence score (0-100).
Adding Context from Previous Nodes:
Use the $$ selector to reference data from any previous node in your workflow:
textExample with context: Alert Data: $$trigger.alert_details User History: $$database_query.user_logs Threat Intel: $$api_call.threat_data Based on the above context, analyze if this is a legitimate threat.
Syntax:
$$nodeName.field- Reference specific fields$$nodeName- Reference entire node output- Works in both System Prompt and User Prompt
🔗 Pro Tip: Add relevant context from previous nodes to help the agent make better decisions. But don't overload - include only what's necessary for the task.
📚 Learn More: Prompt Management
Tools
Tools empower your AI Agent to perform actions beyond thinking and reasoning. By adding action nodes as tools, the agent can intelligently decide when to call them based on the task at hand.
Action Nodes as Tools
You can add various types of actions as tools for your agent. These "Action Nodes" are flexible and can be customized based on your use case by selecting the right integration, writing Python code, or calling external APIs.
Supported Action Types:
| Action Type | Description | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Python Actions | Execute custom Python code | Complex data processing, calculations |
| REST API Actions | Call external APIs | Integrate third-party services |
| Steampipe Actions | Query cloud infrastructure | ⚠️ May cause delays; use sparingly |
💡 Recommendation: Prioritize Python and REST API actions for optimal performance. Steampipe actions can introduce latency during tool execution.
Custom Tools: You can also create custom tools as part of Action Nodes, such as advanced search tools, planning actions (which is using different model for thinking), notification tools, and more, based on your specific use case.
MCP Tools
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Tools are remotely hosted integrations provided by official vendors. These appear in the Actions panel and can be dragged directly into your AI Agent as tools.
Examples of MCP Tools:
- Database connectors
- Cloud service integrations
- Third-party API wrappers
Configuring Tool Parameters
Tool Names & Descriptions
Tool Name: Ensure action names are clear and relevant (e.g., "Search_Customer_Database" rather than "Action_123").
Usage Notes: In the tool’s advanced settings, include descriptions to provide the AI with better context on when and how to use each tool.
Example Usage Note:
textUse this tool to search customer records by email or ID. It returns the customer profile, purchase history, and support tickets.
By default, the description is automatically generated based on the tool’s functionality, but adding this optional detail enhances the AI’s understanding and improves its ability to utilize the tool effectively.
AI-Generated vs Fixed Parameters
Each tool parameter has an AI toggle that controls how values are provided:
| AI Toggle State | Behavior |
|---|---|
| ON (default) | Agent generates parameter value dynamically based on context |
| OFF | Parameter uses your hardcoded value (agent cannot modify) |
When to disable AI:
- ✅ Static values (e.g., always use same API endpoint)
- ✅ Security constraints (e.g., fixed user permissions)
- ✅ Compliance requirements (e.g., specific database to query)
Static Parameters (Non-Modifiable)
Certain parameters are always static and cannot be changed by the agent during tool calls:
- Python Actions: Code content
- REST API Actions: API URL and HTTP method
This ensures security and prevents unintended modifications to core tool behavior.
Built-In Internal Tools
The AI Agent includes specialized internal tools that are automatically available based on your configuration:
💾 save_summary_and_end_chat
Availability: Interactive mode only
Allows users to explicitly ask the agent to close the chat session and complete node execution.
Usage:
textUser: "Save our conversation and close this chat" Agent: [Calls save_summary_and_end_chat tool] Generates summary and output, ends session
In autonomous mode, session ending is handled automatically—no user intervention needed.
🔍 analyse_tool_result
Purpose: Helps agent manage and search through large volumes of tool call results
Capabilities:
- Monitor previous tool executions
- Filter results by criteria
- Search through tool output data
- Embedding search (if embedding model enabled in Preferences)
When it's useful:
- Agent made multiple tool calls and needs to find specific data
- Large result sets that need filtering
- Cross-referencing information from different tools
🌐 duck_duck_go_search
Availability: Enabled via "Use Search" toggle
Allows agent to search the internet using DuckDuckGo search engine.
Use cases:
- Looking up current information
- Verifying facts
- Finding documentation or resources
- Checking latest threat intelligence
🧠 memory_tool
Availability: Enabled via "Use Memory" toggle Requirement: Embedding model must be configured in Preferences
Retrieves context from previous conversations and interactions.
Capabilities:
- Access conversation history
- Recall previous user requests
- Reference earlier decisions or actions
- Maintain continuity across sessions
Setup: Configure embedding model in Settings → Preferences → AI Configuration
Monitoring Tool Execution
Bot Execution Logs
All actions called by the agent are visible in the generated bot execution log:
- ✅ Which tools were called
- ✅ Input parameters provided
- ✅ Output returned from each tool
- ✅ Execution timestamps and duration
- ✅ Success/failure status
Exception: MCP tools called remotely won't appear in bot execution logs.
Chat History
Tool executions are also summarized in the chat history for quick reference during interactive sessions.
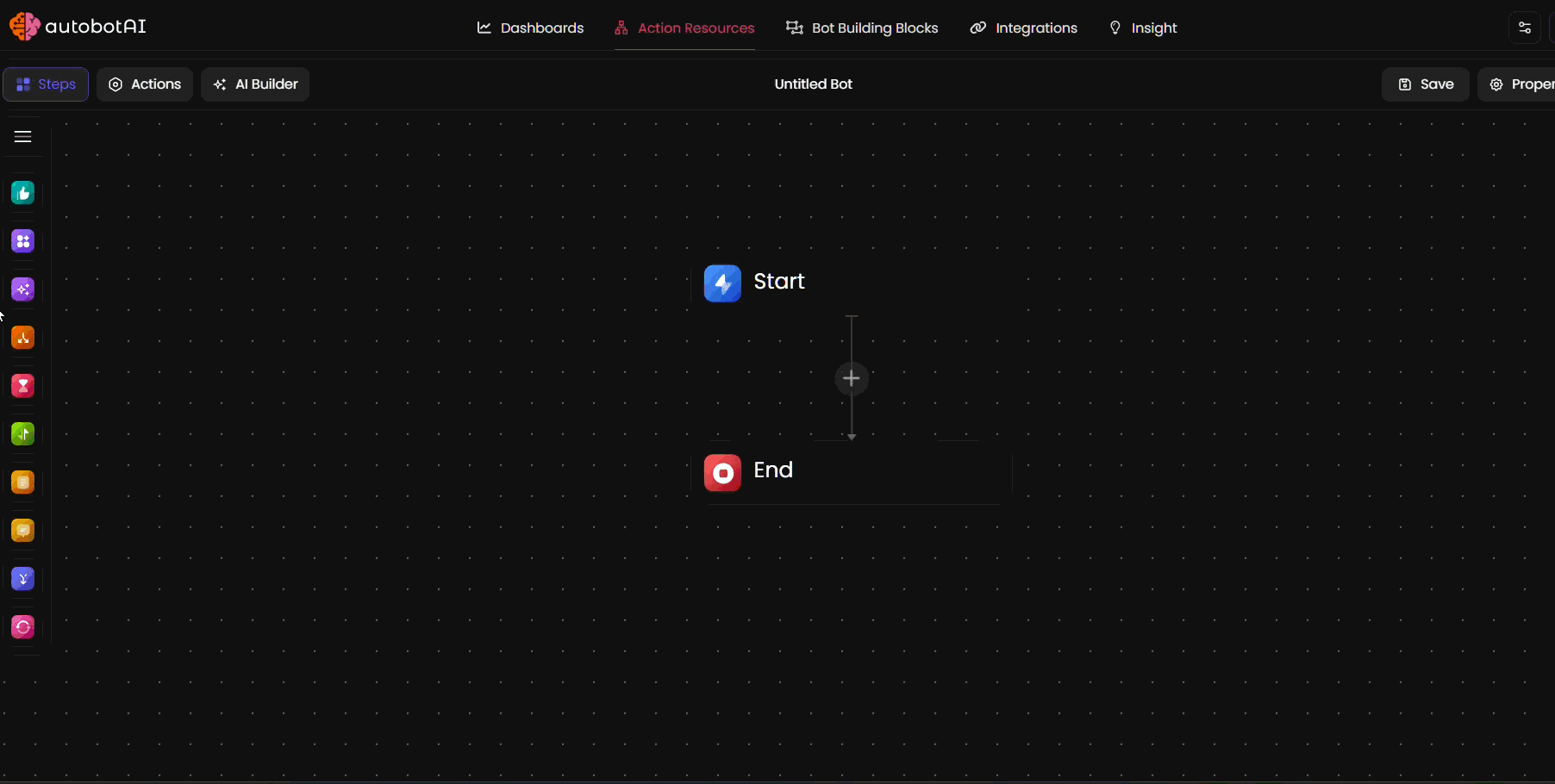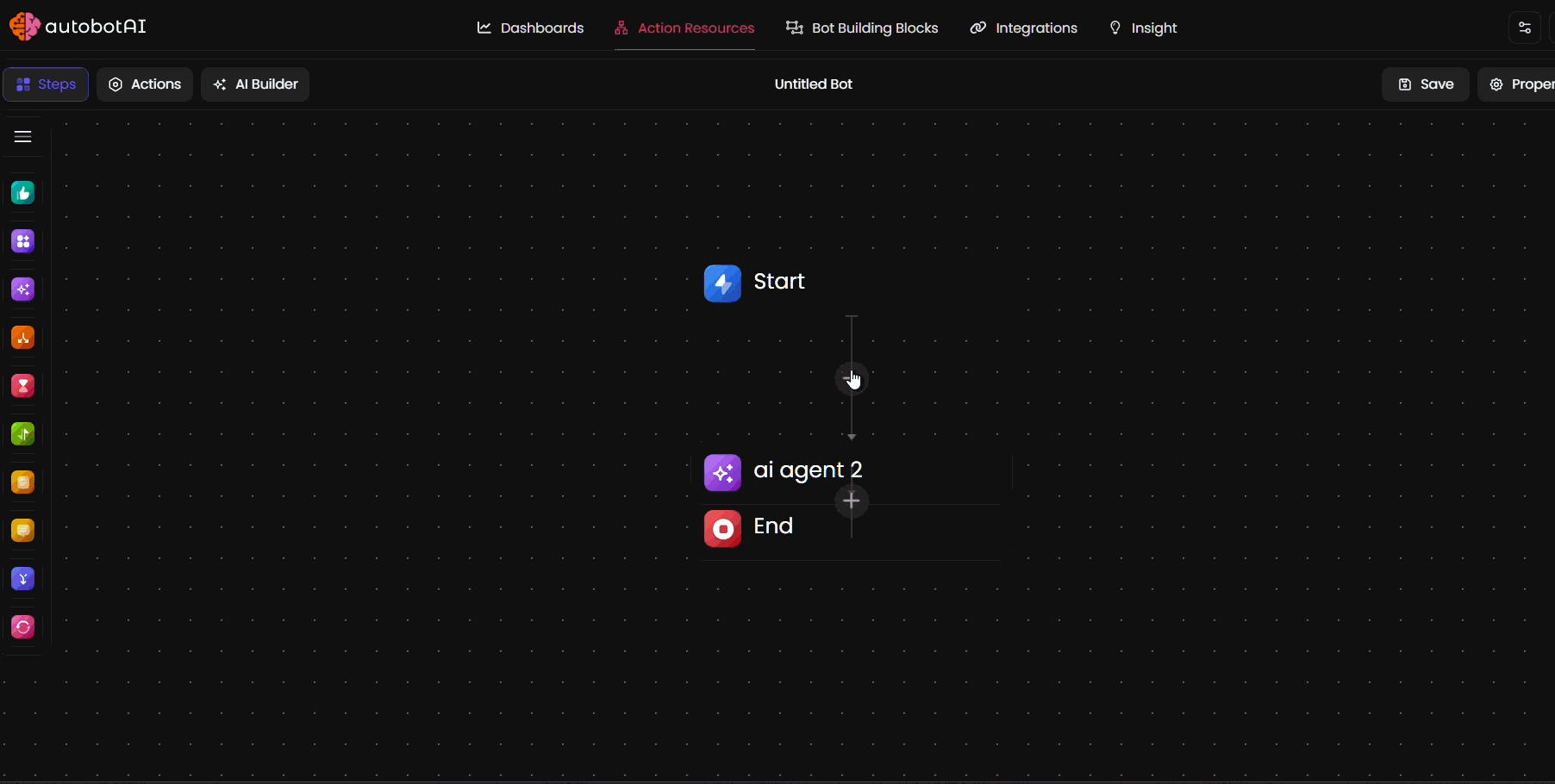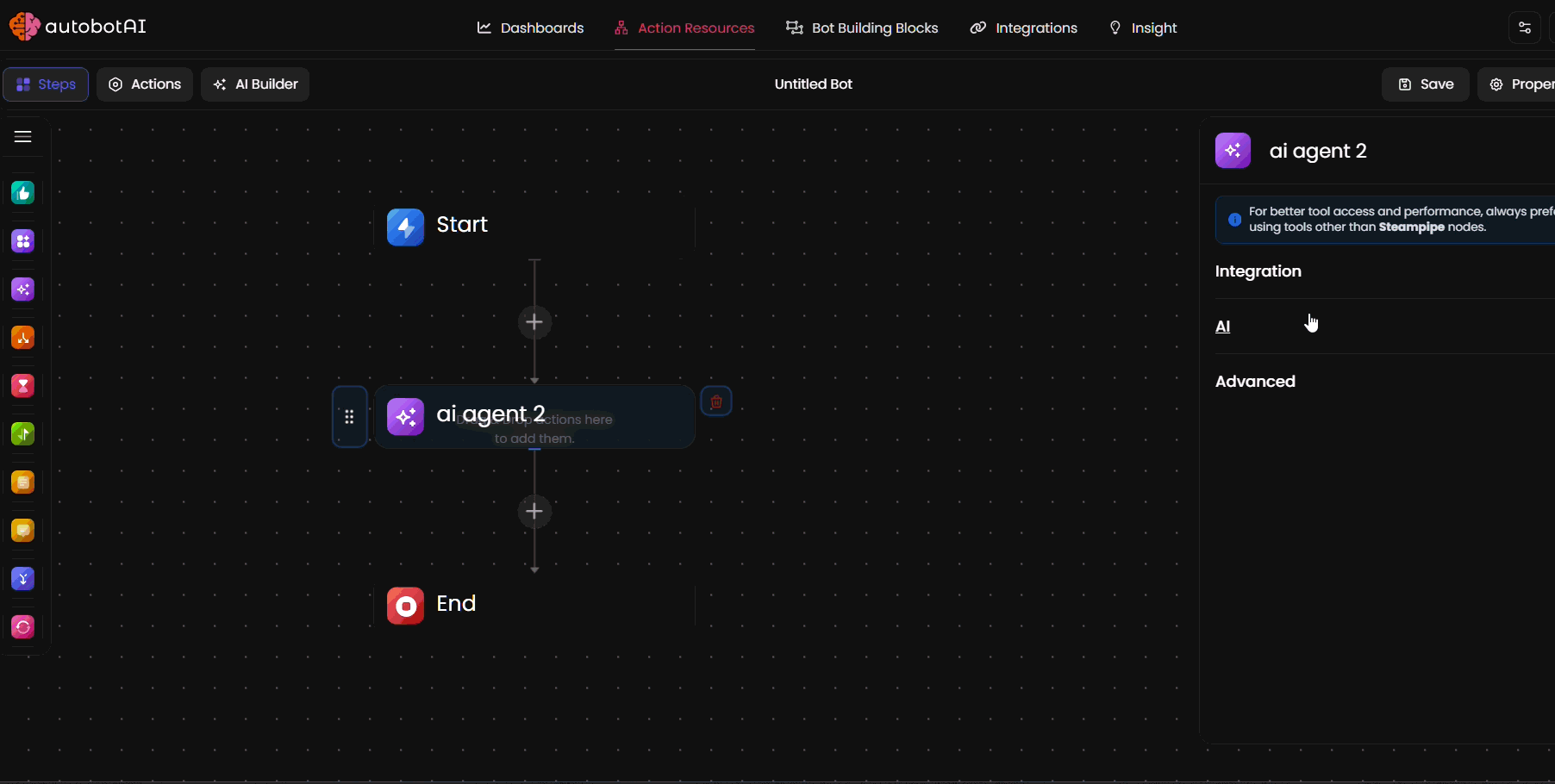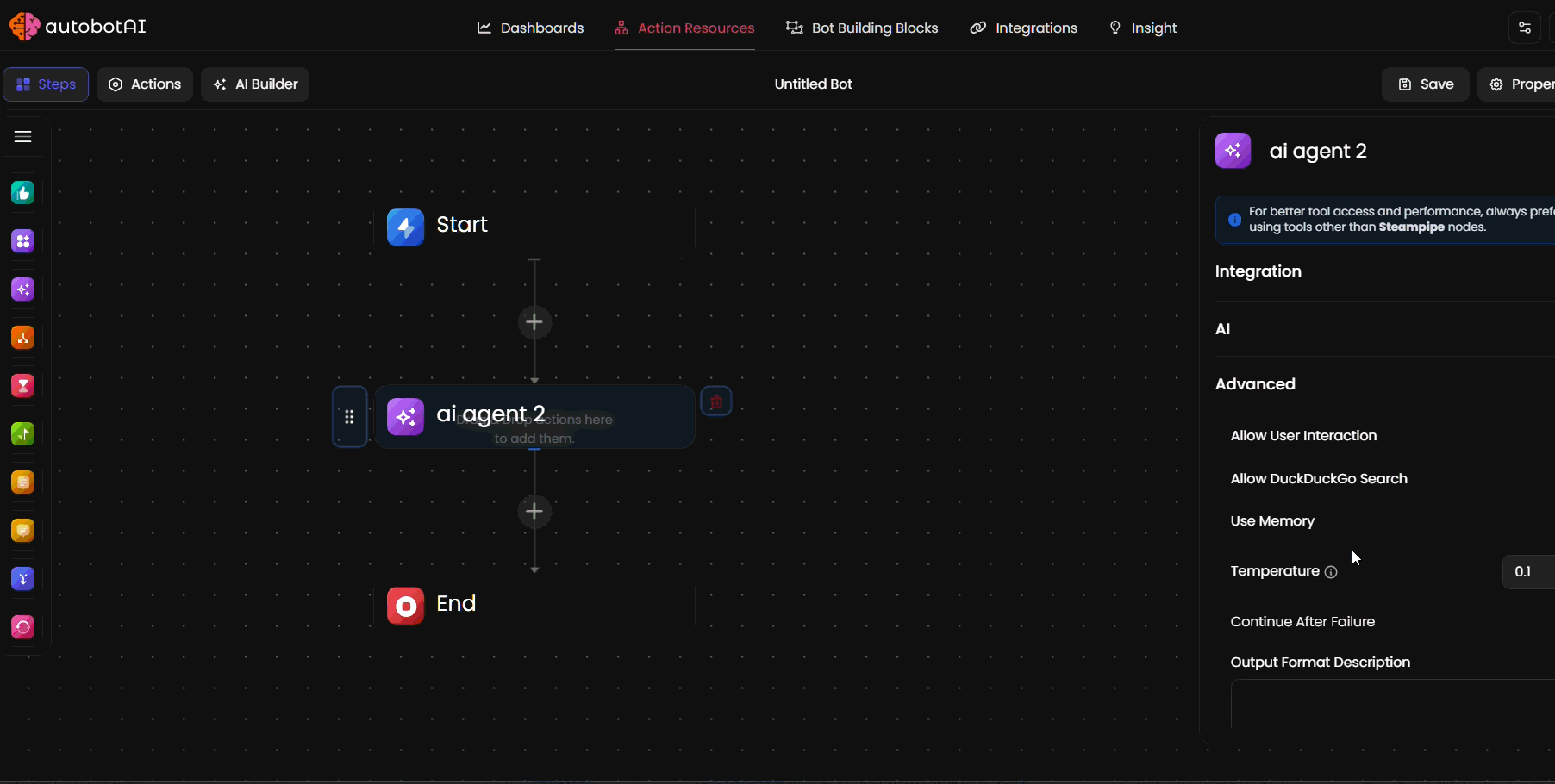
Advanced Settings
Fine-tune your AI Agent's behavior with these optional configurations. These settings allow for greater control over interaction style, reliability, and output consistency.
Allow User Interaction
Toggle to enable interactive mode, allowing back-and-forth conversations with the agent.
Interactive (On):
- Supports multi-turn dialogues
- Agent can ask clarifying questions
- Ideal for: User-facing chatbots, collaborative workflows, or approval processes
Autonomous (Off):
- Runs independently without user input
- Executes tasks in a single pass
- Ideal for: Background automation, batch processing, or silent analysis
💡 Tip: In interactive mode, the agent uses the built-in save_summary_and_end_chat tool to gracefully end sessions when appropriate.
Allow DuckDuckGo Search
Enable this to grant your agent access to the duck_duck_go_search tool for real-time web queries.
When to enable:
- ✅ Fetching current events or threat intelligence
- ✅ Verifying facts or researching external resources
- ❌ Internal data analysis (use dedicated tools instead to maintain privacy)
How it works: The agent intelligently decides when to search based on your prompt, pulling in fresh results to inform its reasoning.
⚠️ Note: Searches are anonymous and privacy-focused via DuckDuckGo. Results are summarized inline in the agent's response.
Use Memory
Toggle on to activate the memory_tool, enabling the agent to recall context from prior interactions.
Benefits:
- Maintains conversation history across workflow steps
- References past decisions for more coherent outputs
- Supports continuity in multi-session scenarios
Requirements: Configure an embedding model in Settings → Preferences → AI Configuration for optimal retrieval.
Temperature
Set the randomness level for the AI's responses (range: 0.0–2.0). Lower values produce more deterministic, focused outputs; higher values encourage creativity.
- 0.0–0.5: Precise and consistent (e.g., for structured analysis)
- 0.7–1.0: Balanced creativity (default for most tasks)
- 1.0+: Exploratory or diverse ideas (e.g., brainstorming)
💡 Tip: GPT-5 models handle temperatures up to 1.0 effectively—start low and adjust based on testing to balance reliability and innovation.
Continue After Failure
Enable this to prevent workflow interruptions from agent errors. If toggled on:
- Individual tool calls or iterations (e.g., in loops) fail gracefully without halting the entire bot execution
- The agent retries or skips problematic steps, logging the issue for review
- Applies to the parent bot execution containing the AI Agent (not any sub-executions triggered by the agent)
Use cases:
- ✅ High-volume processing where partial failures are tolerable
- ❌ Critical paths requiring 100% success (keep off for strict validation)
Best Practice: Always review execution logs for failure details, even in continue mode.
Output Format Description
Specify a structured format for the agent's output to ensure parseable, consistent results in downstream nodes. If left empty, the output field in results will be null.
Why it matters: Mixing free-text instructions with JSON schemas or examples can lead to inconsistent parsing. For reliable results, define a clear JSON Schema—the agent will adhere to it closely.
How Output Is Generated
When an Output Format Description is provided, the system automatically triggers a dedicated output agent after the conversation agent has completed its task and tool calls. This output agent does not participate in the conversation. It uses:
- The full conversation history
- All tools responses collected during the run
…to generate the final structured output according to the format you defined.
If no output format is defined, the output agent will not run and the output field will remain null. The conversation agent still executes normally, including tool calling and decision making.
Pro Tip: Reference the output in later nodes with {{$ai_agent.output.field_name}}.
Writing Effective JSON Schemas
Follow these guidelines to create robust schemas that guide the agent toward precise, validated outputs. A well-defined schema minimizes errors and simplifies integration.
Key Rules:
- Start with the schema declaration: Include the
$schemaline for compatibility. - Define core elements: Always specify
type,properties, andrequiredfields. - Add descriptions: Explain each property clearly to aid understanding.
- Use camelCase for properties: Avoid spaces (e.g.,
firstNameinstead of"First Name"). - Include examples: Demonstrate valid data to reinforce the structure.
Example Schema:
json{ "$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#", "title": "Alert Analysis", "type": "object", "properties": { "is_false_positive": { "type": "boolean", "description": "True if the alert is a false positive." }, "confidence_score": { "type": "number", "minimum": 0, "maximum": 100, "description": "Confidence level (0-100)." }, "reasoning": { "type": "string", "description": "Step-by-step explanation of the decision." } }, "required": ["is_false_positive", "confidence_score", "reasoning"], "example": { "is_false_positive": true, "confidence_score": 85, "reasoning": "Source IP matches known benign scanner; no payload indicators." } }
Common Pitfalls:
| Issue | Impact | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Spaces in property names | Parsing errors in tools | Use camelCase (e.g., userId) |
| Missing field descriptions | Ambiguous outputs | Add a description for every property |
Omitting type in objects | Invalid schema | Explicitly set "type": "object" |
Incorrect required array | Incomplete validation | List only essential fields |
💡 Best Practice: Test schemas with sample prompts to verify consistency. For complex outputs, iterate incrementally.
Common Use Cases
🛡️ Security Alert Triage
Scenario: Automatically analyze security alerts to reduce false positives
Configuration:
- System Prompt: "You are a SOC analyst. Evaluate security alerts for legitimacy."
- User Prompt: "Analyze this alert: {{$trigger.alert_data}}"
- Tools: Enable "Check Threat Database" and "Get User Context" nodes
- Memory: Off (each alert is independent)
Output: True/false positive determination with confidence score
📊 Data Enrichment
Scenario: Add context and insights to raw data
Configuration:
- System Prompt: "Enrich data with relevant context and insights."
- User Prompt: "Analyze this data: {{$previous_node.data}} and add business context"
- Tools: Enable "Database Query" and "API Call" nodes
- Memory: On (maintain context across records)
Output: Enhanced data with additional fields and insights
✉️ Intelligent Routing
Scenario: Route tickets or requests to the right team
Configuration:
- System Prompt: "Categorize support tickets by urgency and topic."
- User Prompt: "Categorize: {{$trigger.ticket_content}}"
- Tools: None needed
- Output Format:
json{ "$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#", "title": "Ticket Routing", "type": "object", "properties": { "category": { "type": "string", "description": "Topic or type of the support ticket." }, "urgency": { "type": "string", "description": "Urgency level of the ticket.", "enum": ["low", "medium", "high"] }, "assigned_team": { "type": "string", "description": "Team or department the ticket should be routed to." } }, "required": ["category", "urgency", "assigned_team"], "example": { "category": "billing", "urgency": "high", "assigned_team": "finance_support" } }
Output: Structured routing information for next workflow step
💬 Content Generation
Scenario: Generate reports, summaries, or responses
Configuration:
- System Prompt: "Create clear, professional security reports."
- User Prompt: "Generate incident report for: {{$analysis.findings}}"
- Memory: On (reference earlier findings)
- Output Format: Markdown document structure
Output: Formatted report ready to send
Troubleshooting
Agent returns unexpected results
Possible causes:
- Prompt is too vague or ambiguous
- Wrong model selected for the task complexity
- Missing context from previous nodes
Solutions:
- Refine your prompts with more specific instructions
- Add examples of expected output in system prompt
- Verify input data is correctly referenced with
{{}} - Test with different models to find best fit
Output format not followed
Possible causes:
- Output format description unclear
- Model struggles with complex schemas
- Prompt conflicts with format requirements
Solutions:
- Simplify output format structure
- Explicitly mention format in user prompt: "Return response in this exact JSON format: {format}"
- Use stricter models (GPT-5 or GPT-4o over GPT-3.5)
- Add format example in system prompt
Tool not being called
Possible causes:
- Tool not properly enabled in settings
- Agent doesn't understand when to use the tool
- System prompt doesn't mention tool availability
Solutions:
- Verify tool is selected in Advanced Settings
- Update system prompt: "You have access to these tools: [list tools]. Use them when you need additional information."
- Make user prompt more explicit about when tool usage is needed
Memory & Embedding Setup
To use the memory feature, you need to configure an embedding model:
Global Configuration
- Go to Settings → Preferences
- Navigate to AI Configuration
- Select Embedding Model
- Choose your provider and model
- Save settings
Examples
Example 1: False Positive Detector
Goal: Analyze WAF alerts and filter false positives
yamlIntegration: OpenAI Model: GPT-4o System Prompt: | You are a WAF security analyst. Analyze alerts and determine if they are false positives based on patterns, source reputation, and context. User Prompt: | Alert Details: {{$trigger.alert}} Source IP: {{$trigger.source_ip}} Is this a false positive? Provide your analysis. Tools: - IP Reputation Check - Historical Alert Search Memory: Enabled Agent Type: Autonomous Output Format: | { "$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#", "title": "False Positive Analysis", "type": "object", "properties": { "is_false_positive": { "type": "boolean", "description": "True if the alert is determined to be a false positive." }, "confidence": { "type": "number", "minimum": 0, "maximum": 100, "description": "Confidence score (0–100) in the false-positive determination." }, "reasoning": { "type": "string", "description": "Explanation of how the decision was reached." }, "action": { "type": "string", "enum": ["block", "allow", "review"], "description": "Recommended action based on the analysis." } }, "required": [ "is_false_positive", "confidence", "reasoning", "action" ], "example": { "is_false_positive": true, "confidence": 87, "reasoning": "Source IP is from a trusted scanning provider and behavior matches known benign patterns.", "action": "allow" } }
Example 2: Customer Support Triage
Goal: Categorize and route support tickets
yamlIntegration: OpenAI Model: GPT-3.5 (fast & cost-effective) System Prompt: | Categorize support tickets by department, urgency, and sentiment. Be consistent. User Prompt: | Ticket: {{$trigger.ticket_body}} Categorize this ticket. Memory: Disabled Agent Type: Autonomous Output Format: | { "$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#", "title": "Customer Support Triage", "type": "object", "properties": { "department": { "type": "string", "enum": ["sales", "technical", "billing"], "description": "Which team should handle the ticket." }, "urgency": { "type": "string", "enum": ["low", "medium", "high"], "description": "Urgency level of the issue." }, "sentiment": { "type": "string", "enum": ["positive", "neutral", "negative"], "description": "Emotional tone of the user's message." }, "summary": { "type": "string", "description": "Short summary of the ticket content." } }, "required": ["department", "urgency", "sentiment", "summary"], "example": { "department": "technical", "urgency": "high", "sentiment": "negative", "summary": "User cannot log in and the issue blocks them from accessing their dashboard." } }
FAQs
Q: Can I use multiple AI Agent nodes in one workflow? A: Yes! Chain multiple agents for complex workflows. For example: one agent analyzes, another formats the output.
Q: What's the difference between tools and memory? A: Tools let the agent perform actions (call other nodes). Memory lets it remember previous conversation context.
Q: How do I reference output from the AI Agent in later nodes?
A: Use {{$ai_agent_node_name.output}} or the specific field from your output format.
Q: Can the agent access the internet? A: Only if you enable "Allow DuckDuckGo Search" in advanced settings. Otherwise, it only knows what's in its training data and your prompts.
Q: Is my data secure? A: Data is sent to your configured AI provider (OpenAI, AWS, etc.). Check your provider's security policies. For sensitive data, consider using AWS Bedrock with private endpoints.
Q: How long does the agent take to respond? A: Typically 2-10 seconds depending on model complexity and prompt length. Faster models (GPT-3.5, Claude Haiku) respond in 1-3 seconds.
Additional Resources
Need Help? Contact support at support@autobotai.com
Last updated: November 21, 2025